What is Adjective?
An Adjective is a word used to modify or add some extra meaning to the Noun or Pronoun. In other words, an Adjective describes some qualities of a Noun or Pronoun.
Examples Of Adjective
Study the following sentence:
- The young man is wearing a black shirt.
- The fat boy has black cat with him.
- Good students respect their teacher.
- The thin man is carrying a small box.
- The tall lady is very beautiful.
- This is a big house.
- He is a poor man but he is honest.
- Pavani is an honest woman.
- See, the tall building image below.
The above sentences with bold letters: young, black, fat, black, good, thin, small, tall, beautiful, big, poor, honest, and tall are adjectives. Above all, the adjectives either tell some quality of the noun or pronoun or add extra meaning to them.

Kind of Adjectives | Types of Adjectives
Importantly, There are 06 types of Adjectives. These are as follows:
- Adjective of Quality
- Adjective of Quantity
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Adjective of Number
- Interrogative Adjective
- Possessive Adjective
1. Adjective of Quality
An Adjective of Quality defines the quality of a person or thing. For instance:
- My neighbor is an angry man but honest one.
- Ashok the great was a great emperor.
- Mr. Narendra Modi is not only a famous in India but also in the whole world and he is an inspiring leader.
- As it is a sunny day so I like it.
The Adjectives-Angry, honest, great, famous, inspiring, and sunny tell us what kind of a person or thing is. It answers the question: What kind of?
2. Adjective of Quantity
An Adjective of quantity describes the Quantity of a thing. For example:
- We have much water and sufficient food.
- My brother ate the whole mangoes and banana.
- I want some money.
- There is enough rations for this week.
The Adjective-much, sufficient, whole, some, and enough tell us how much of something is there or available, intended or required. Therefore, Such Adjectives are called Adjectives of Quantity. Mainly, this adjective answers the question: How Much?
3. Demonstrative Adjectives
A Demonstrative Adjective points out or demonstrates some person or things. Generally, This, that, these, those, and such, etc., are the Demonstrative Adjective. Study the following examples:
- I do not like such behavior.
- This was my first attempt but I could crack the examination .
- That is my car.
- These books are belong to one of my friends Narayan. But, those are not mine.
- Those books are yours and These books are mine.
Such, This, That, These, and Those– Adjectives refer to which person or things are meant. Therefore, such types of adjectives are called Demonstrative Adjective. Above all, this type of Adjective answers the question: Which?
4. Adjective of Number
An Adjective of Number tells us how many persons or things are there. Further, it also tells in what order the person and things stand. For instance
- I have three cars and two motor-bikes.
- Many women are clearing U.P.S.C examination.
- Hundreds of people gathered at Mahatma Gandhi’s funeral.
- The first girl won the prize but the last one could not.
The above Adjectives in bold letters-three, many, hundreds, first tell us how many persons or things are meant. That is to say, the Adjective of Number answers the question: How many?
5. Interrogative Adjectives
Words like-What Which, When, Where, Whose, etc., when used with nouns to ask questions; are defined as Interrogative Adjective.
Look at the examples given below.
- What time is it?
- Which color do like the most?
- Whose books are those and why those books are still there since morning?
- Which type of movies and drams you like the most?
In the above sentences what, which, Whose, and Which are used with nouns viz: time, colour, books, and type of movies and dramas (NP) to ask questions. As a result, these words with nouns become Interrogative Adjective.
6. Possessive Adjectives
The Possessive Adjective indicates possession or belonging of something. In other words, words like-my, his, our, and your with a noun or noun phrases become Possessive Adjectives.
Read the following examples:
- He is my younger brother and his score in Mathematics is better than me.
- Your and my parents know each other before.
- I thought this bicycle belongs to her but it belongs to her brother.
- His book has been mixed with their books and have been submitted to library.
- The Possessive Adjective of it is its.
- The Possessive Adjective Your is used for both singular and plural.
My, his, your, her, his, their, and its are Possessive Adjective.
Comparison of Adjectives | Degrees of Comparison of Adjective
There are 03 degrees of comparison of adjectives. Which are as follows:
- Positive degree of adjective,
- Comparative degree of adjective, and
- Superlative degree of adjective
1. Positive Degree of Adjective
The ordinary form of an adjective is called the Positive degree of Adjective. To clarify, study the following examples:
- Gopal is a tall boy.
- Suresh is a good dancer and singer.
- Mamata is a beautiful girl.
2. Comparative Degree of Adjective
When two things of the same class/group/category are compared; we use the Comparative degree of adjective. In other words, if we use an adjective to compare then it is called Comparative Degree of Adjective.
Study the following examples:
- Manish is taller than Gopal.
- Muna is better than player than Sonu.
- Ronika is more beautiful than Joshna.
Importantly, Comparative Degree of Adjectives takes than after them.
3. Superlative Degree of Adjective
When one thing is compared with all other things of the same class/group/category, we use the superlative degree of adjective. For better understanding, read the following examples:
- Rohan is the tallest boy in our class.
- John is the best player in our team.
- Madhu is the most beautiful girl in her family.
- This is the best book that I have ever read.
The superlative degree of adjectives takes the before them.
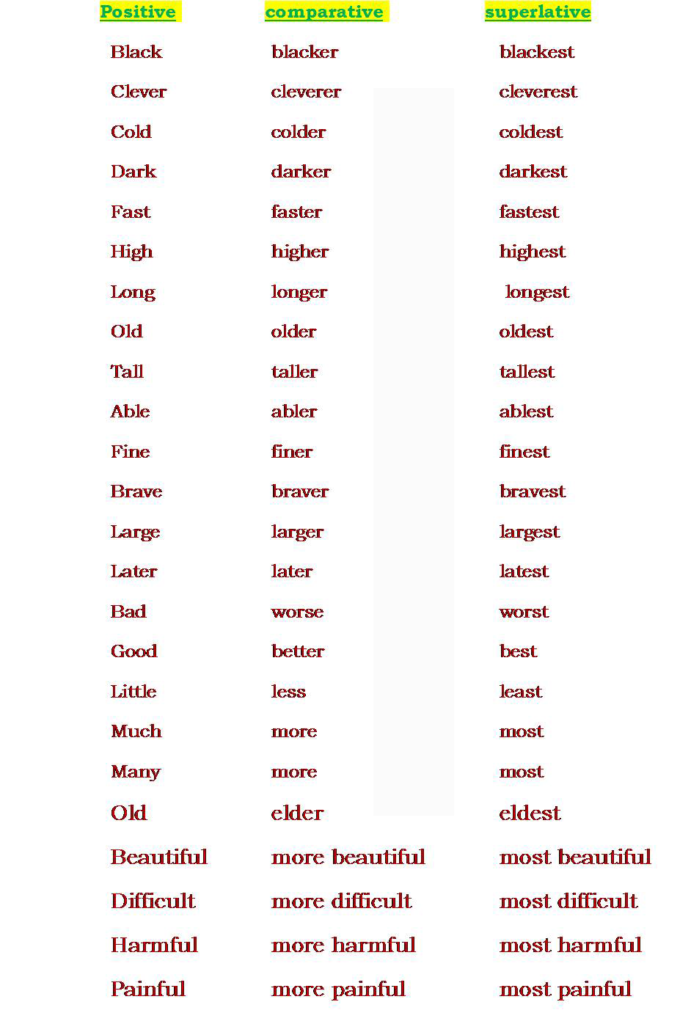
List of Positive, Comparative and Superlative Degree Adjectives.
Adjectives and their opposites

Exercise for Adjective | Adjective Exercise
- Give the comparative and superlative following adjectives:
Deep, Happy, poor, risk, late, sad, thin, many, famous, bright, old, bad, dirty, cold, big, painful, busy, lucky, wise, blunt, and dear.
- Give the opposite of the following adjectives:
Thin, sharp, ugly, stupid, beautiful, easy, bright, thin, poor, young, low, dirty, small, hot, wet, full, sweet, hard, clean, lucky, fortunate, Innocent, plentiful, boastful, impolite, foolish, modern, cowardly, generous, cloudless, noisy, and regular.
- Find out the adjective and name their degree of comparison.
- Delhi is the hotter than Shimla.
- Ashok was a great king.
- Ramesh is the tallest boy in our class.
- Who is the best player of your team?
- Nisha is slower than Rina but Rina is more beautiful than Nisha.
- She was wearing a blue fork.
- This is an easy question.
- He got more marks than Ritika.
- Which is the longest river of India?
- Supply the proper form [Comparative or Superlative] of the given adjective.
- May is ____than April.(hot)
- Your knife is sharp, but mine is__________. (sharp)
- This pen is _______than the other. (good)
For more click on the link: Adjective
I have found that if you love life , life will love you back
-The Secret,

